Introduction:
The upcoming Wi-Fi 7 standard, based on IEEE 802.11be technology, is poised to revolutionize wireless networking in diverse environments, from homes to industries. In a recent announcement on the Wi-Fi Alliance website, it is revealed that Wi-Fi 7 certification is expected to be finalized by the end of the first quarter of 2024, ushering in a new era of connectivity and advanced performance.
 Certification Timeline:
Certification Timeline:
The Wi-Fi Alliance, an influential industry group setting Wi-Fi standards, emphasized in its post that Wi-Fi Certified 7 devices will be available before the close of Q1 2024. This certification is crucial for ensuring global interoperability, fostering the adoption of Wi-Fi 7, and delivering cutting-edge capabilities to the next generation of connected devices.
Performance Advancements:
Wi-Fi 7 is set to outpace its predecessor, Wi-Fi 6 and 6E, with significantly increased speeds. Kristen Hanich, an analyst with Parks Associates, highlighted Wi-Fi 7’s key feature—support for extremely high throughput, reaching speeds up to 46 Gbps, a considerable leap from the 10 Gbps maximum of Wi-Fi 6E. The enhanced speeds will particularly benefit applications requiring high throughput, lower latency, and greater reliability.
Dynamic Band Switching Advantage:
A standout feature of Wi-Fi 7 is multi-link operation (MLO), lauded by Andrew Spivey, a senior analyst with ABI Research. MLO addresses spectrum congestion challenges by improving spectrum efficiency through the aggregation of multiple radio links. This allows dynamic connections to multiple bands, overcoming the limitations of traditional band selection
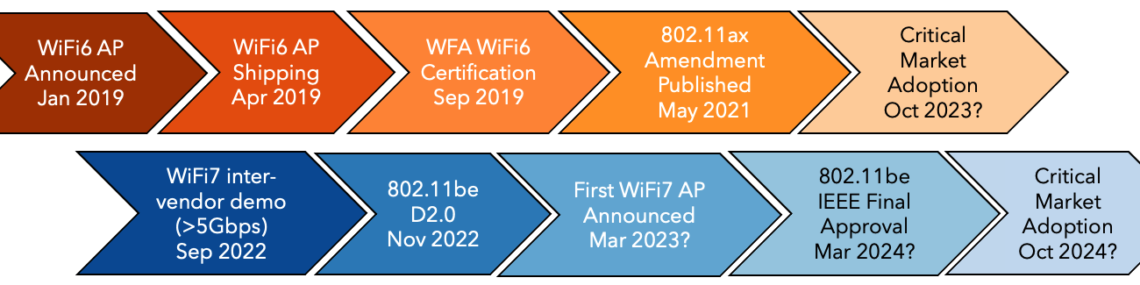 Access to 6 GHz Band:
Access to 6 GHz Band:
Wi-Fi 7’s compatibility with the recently released 6 GHz band effectively doubles the available spectrum in the U.S., addressing spectrum congestion challenges and expanding capacity. The adoption of Wi-Fi 7 is expected to facilitate a smoother transition to the new band, thereby improving overall network performance.
Market Dynamics and Competition:
The Wi-Fi Alliance’s recent trend of accelerating standardization aligns with the rapid adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and 6E. Over half of Wi-Fi-enabled devices shipped in 2022 were Wi-Fi 6 or 6E certified. While Wi-Fi 6 demand continues, Wi-Fi 7 is anticipated to gain traction swiftly due to its innovative features, including increased network capacity.
Competitive Landscape:
As the next-generation Wi-Fi 7 standard prepares to make its mark, it finds itself navigating a competitive landscape dominated by its predecessors, notably Wi-Fi 6 and 6E. Understanding the intricacies of this competitive terrain is crucial to foreseeing the challenges and opportunities that Wi-Fi 7 will encounter on its journey to widespread adoption.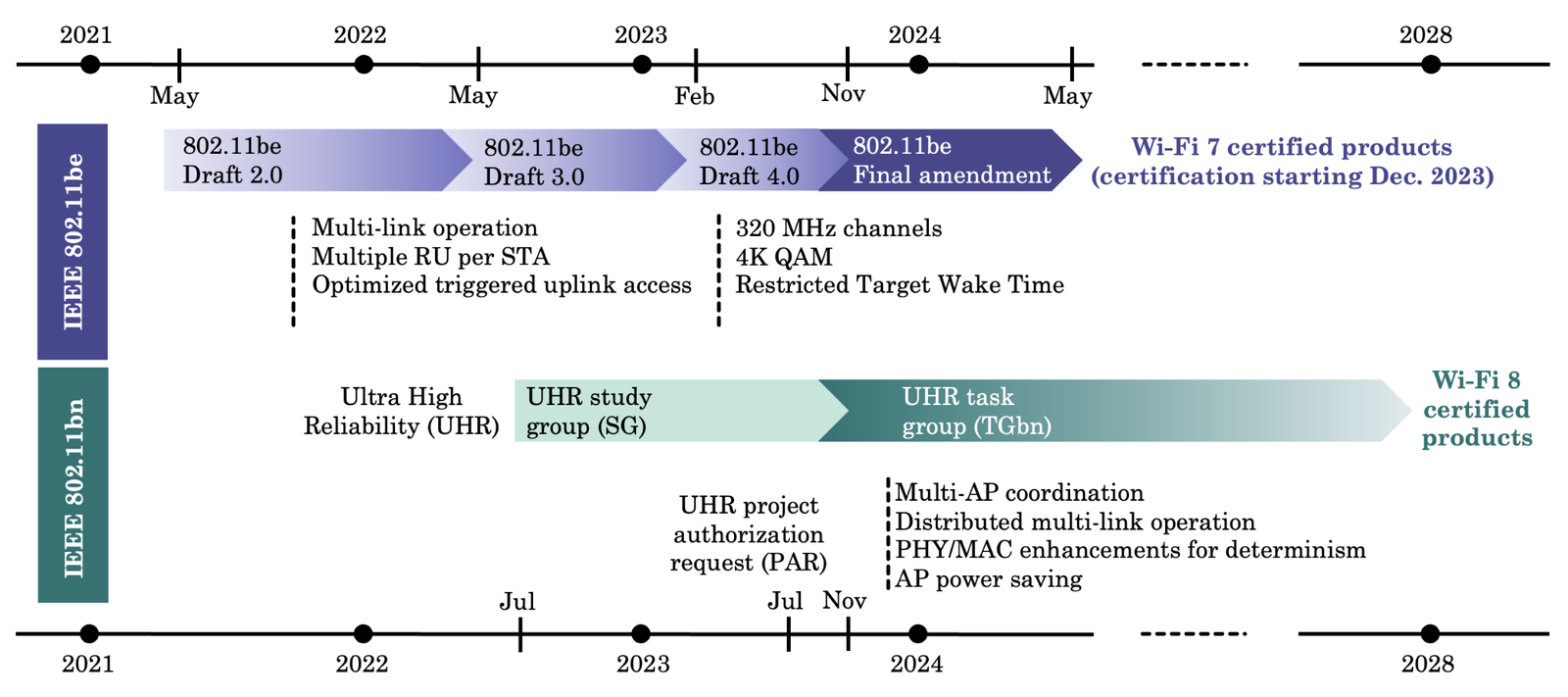
1. Historical Momentum: Wi-Fi 6 and 6E have established a strong foothold in the market since their introductions in 2019 and 2021, respectively. The Wi-Fi Alliance reported that over half of Wi-Fi-enabled devices shipped in 2022 were certified under these standards, indicating a significant market presence. The rapid adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and 6E, fueled in part by the global chip shortages, created an environment where these standards gained momentum quickly.
2. Unique Circumstances of Adoption: Wi-Fi 6 and 6E’s initial success can be attributed to unique circumstances, such as the scarcity and high cost of Wi-Fi 5 chipsets. This scarcity incentivized consumers and industries to opt for the latest standards, driving the adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and 6E. Wi-Fi 7, in contrast, lacks this advantage and will need to contend directly with the established user base of its predecessors, particularly Wi-Fi 6 and 6E.
3. Bandwidth Discrepancy and Niche Markets: While Wi-Fi 7 boasts dramatically higher bandwidth compared to Wi-Fi 6E, surpassing the current needs of the majority of consumers, it positions itself as a specialized solution catering to specific niches. Applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and enterprise environments, where the demand for rapid data transfer is pronounced, are expected to be key markets for Wi-Fi 7. Balancing this niche orientation with the broader consumer demands will be a strategic challenge for Wi-Fi 7.
4. Market Dynamics and Technology Leap: The Wi-Fi Alliance’s recent trend of accelerating standardization, as witnessed in the swift adoption of Wi-Fi 6E, adds an additional layer of complexity to the competitive landscape. Wi-Fi 7, while not an immediate successor in the vein of 6E, brings substantial technological advancements, making it more in line with the traditional progression seen in Wi-Fi generations. Balancing the market’s appetite for the latest technology with the incremental nature of Wi-Fi 7’s improvements poses a challenge in differentiating it from its predecessors.
5. Pent-up Demand for Advanced Features: Anticipation for Wi-Fi 7 has been palpable throughout 2023, suggesting a pent-up demand for the advanced features it promises. Multi-link operation (MLO) and access to the 6 GHz band are touted as game-changers that can alleviate spectrum congestion challenges. However, Wi-Fi 6E’s slow deployment in the year preceding Wi-Fi 7’s arrival indicates a widely held belief that 6E was merely a steppingstone standard, paving the way for the more comprehensive Wi-Fi 7.
6. Long-Term Integration Challenges: Gaining certification from the Wi-Fi Alliance marks only the initial phase of Wi-Fi 7’s market journey. The road to widespread adoption is traditionally a gradual process, typically taking two to three years. Factors such as device availability, cost considerations, perceived benefits, and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns will play pivotal roles in determining how quickly Wi-Fi 7 becomes an integral part of the wireless ecosystem.
Market Integration Challenges:
Gaining certification from the Wi-Fi Alliance is just the initial step in Wi-Fi 7’s market journey. The integration process is expected to take two to three years for widespread adoption, influenced by factors such as device availability, cost, perceived benefits, and marketing efforts. Wi-Fi 7’s unique features may lead to a slower but impactful integration into the broader ecosystem.
Conclusion:
Wi-Fi 7, with its advanced features and enhanced performance, is on the horizon, promising to reshape wireless connectivity. As it undergoes certification and enters the market, its impact on diverse sectors, from consumer electronics to industrial applications, is poised to be profound, paving the way for a new era of seamless and high-performance wireless communication.
Read more: